| Lean Manufacturing is a systematic way to deliver
the :
- highest quality,
- lowest cost products with the
- shortest lead-times through the
- relentless elimination of waste.
Lean manufacturing is simply a continuously
progressive way of producing what the customer
wants, when they want it, at a price they are
prepared to pay and using least resources
HISTORY OF LEAN
- Lean manufacturing was developed by the Japanese automotive
Industry, principally Toyota, following the challenge to re-build the
Japanese economy after World War-II.
- The development of Lean was little known or understood outside
Japan until the1970’s. Britain gained early experience of Lean
manufacturing from the establishments of Toyota, Nissan and
Honda plants in UK.
- Nevertheless, until the 1990s it was really only the automotive
industry that had adopted Lean manufacturing. Since then it has
spread into aerospace and general manufacturing, consumer
electronics, healthcare, construction and, more recently, to food
manufacturing and meat processing.
LEAN Principles
- Specify the value desired by the customer;
- Identify the value stream for each product providing that
value and challenge all of the wasted steps (generally nine out
of ten) currently necessary to provide it;
- Make the product flow continuously through the remaining
vale-added steps;
- Introduce pull between all steps where continuous flow is
possible; and
- Mange toward perfection so that number of steps and the
amount of time and information needed to serve the
customer continually falls.
World Class Manufacturing and Measurements that drive Customer Satisfaction
World Class Performance Goals |
Lean Manufacturing Technique Used to Achieve |
Zero-Lost Time Accidents |
· 5 S
· Visual Communication |
Zero-Unplanned Downtime
|
· 5 S
· Total Productive Maintenance(TPM) |
Zero-Scrap /Rework
|
· 5 S
· Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
· Manufacturing Cells / One Piece Flow
· Setup Reduction
· 5 S |
Zero-Setup Time
|
· Setup Reduction |
Zero-Inventory
|
· Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
· Manufacturing Cells / One Piece Flow
· Setup Reduction
· Kanbans |
100% Participation
|
· Leadership & Empowerment
· 5 S & Kaizen
· Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
· Manufacturing Cells / One Piece Flow
· Setup Reduction
· Kanbans |
Types of Wastes
The elimination of waste is the goal of Lean, and Toyota
defined three broad types of wastes: muda, muri and mura
(3Ms).
- Muri focuses on the preparation and planning of the
process, or what work can be avoided proactively by design.
- Mura focuses on how the work design is implemented and
the elimination of fluctuation at the scheduling or
operations level, such as quality and volume.
- Muda is traditional general Japanese term for activity that is
wasteful and doesn't add value or is unproductive
The Original Seven Mudas
- Transportation
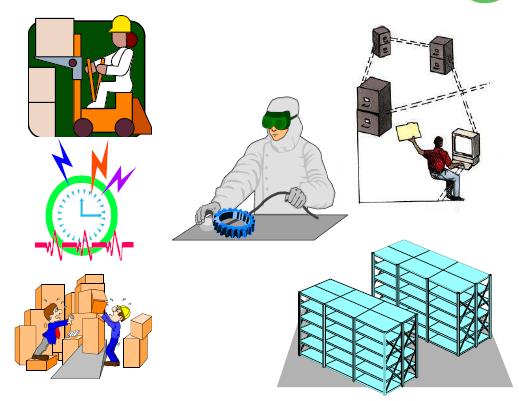
- Inventory
- Motion
- Waiting
- Overproduction
- Over Processing
- Defects
Later an eighth waste described as manufacturing goods or services that do not meet customer demand or specifications.
Lean Manufacturing Tools & Techniques
- 5S System
- Visual Control
- Just in Time (JIT)
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Cellular Manufacturing Technology
- Value Stream Mapping
- Poke Yoke or Mistake Proofing
- Single Minutes Exchange of Dies
- Kaizen
- Kanban
- Machine Capability Studies
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- Six Sigma
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing Scheme
- Reduction in waste;
- Improvement in productivity and quality;
- Introduction of innovative practices for improving overall competitiveness;
- Induce good management practices (GMP);
- Increase in manufacturing output
- Reduction in customer complaints
- Better and improved adherence to delivery schedule
- Reduction in quality rejection at every stage of production process
- Lesser inventory requirements at every stage of production
- Optimum utilization of resources in terms of space, manpower, material,
- equipment utilization and energy consumption
- Orderly work place
- Imbibe a culture of continuous improvement
5 S
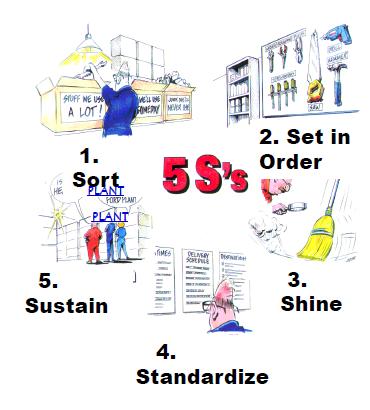 |
The 5 S concepts consistently produce an organized workplace, resulting in
- An increase in quality
- An increase in productivity
- A cleaner and safer workplace
- A reduction in required floor space.
|
VISUAL Control
Visual systems are a form of communication and can be used to direct flow and identify problems/needs/status with minimal interaction from a person. Simple signals that provide an immediate
understanding of a situation or condition such as charts, light signals, Lane marking on floor, Safety instructions, Warning signs etc |
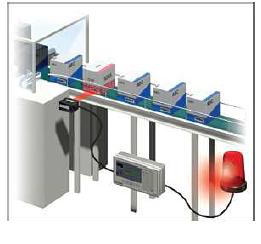
|

JUST IN TIME (JIT)
JIT manufacturing is a philosophy of manufacturing based on
planned elimination of waste & continuous improvement of
pr oductivity. It aims at producing the right product in right oductivity. It aims at producing the right product in right
quantity at the right time. This almost results in zero
inventory and shortest possible cycle time.
The application of JIT in Lean
Manufacturing leads to:
•Reduction in inventory by more than 50%
•Reduction in lead times by more than 50%
•Reduction in rework
•Reduction in space by more than 40%
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
An SOP is a written document / instruction detailing all steps
and activities of a process or procedure. All quality impacting
processes and procedures should be laid out in Standard
Operating Procedures (SOPs). These SOPs should be the basis
for the routine training program of each employee.
Cellular Manufacturing Technology
A manufacturing cell or work cell comprises a group of
equipment,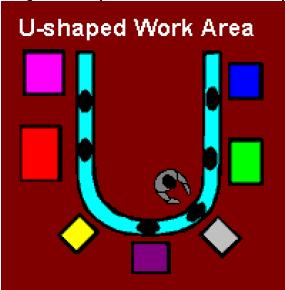 usually laid out in the shape of a “U” that is
dedicated to the complete production of a family of similar
parts. These manufacturing cells produce parts, one at a time,
by linking together a sequence of machine or assembly
operations in a smooth production flow known as One Piece
Flow Production. usually laid out in the shape of a “U” that is
dedicated to the complete production of a family of similar
parts. These manufacturing cells produce parts, one at a time,
by linking together a sequence of machine or assembly
operations in a smooth production flow known as One Piece
Flow Production.
Value stream mapping
Value stream mapping is a Lean technique used to analyze
the flow of materials and information currently required to
bring a product or service to a consumer. Value stream
mapping is commonly used in Lean environments to identify
opportunities for improvement in lead time.
Although value stream mapping is often associated with
manufacturing, it is also used in logistics, supply chain,
service related industries, product development etc.
Poke Yoke Mistake Proofing
It is a Japanese technique used to prevent errors occurring at
their source of origin, and it finally leads to a 'Zero Defect'
situation. The idea behind Poke Yoke is to free a person’s
mind from maintaining repetitive vigil which may be
practically not feasible. It is extremely cost-effective lean
manufacturing tool, using very simple devices to prevent the
production of defective products. 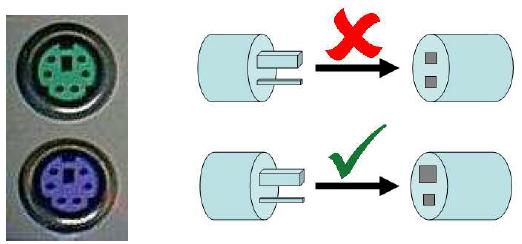
Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)or Quick ChangeOver
Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) is one of the many lean
production methods for reducing waste in a manufacturing
process. It provides a rapid and efficient way of converting a
manufacturing process from running the current product to
running the next product. This rapid changeover is key to
reducing production lot sizes and thereby improving flow .The
phrase "single minute" does not mean that all changeovers and
startups should take only one minute, but that they should take
less than 10 minutes. Primarily it enables a manufacturing
organisation to move from a "minimum batch quantity"
approach to a "batch of one" approach. lot sizes and thereby improving flow .The
phrase "single minute" does not mean that all changeovers and
startups should take only one minute, but that they should take
less than 10 minutes. Primarily it enables a manufacturing
organisation to move from a "minimum batch quantity"
approach to a "batch of one" approach.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
TPM focuses on the objective of zero breakdowns. Significant
emphasis is given on first line preventive maintenance by
operators, which is then supported by a regime of preventive
maintenance provided by specialists
The benefits of TPM implementation are:
- Improve productivity
- Reduce breakdown leading to Zero Breakdown concept
- Leads to multi-skilling of workers
- Better safety
- Improve quality of products.
Kaizen
Kaizen is a Japanese word meaning "improvement," that calls for
never-ending efforts to improve, inviting each and every one in
the organization to take part. Doing “little things “better
everyday defines Kaizen- slow, gradual but constant
improvements-continuous improvement in any area that will
eliminate waste and improve customer satisfaction.
The target of Kaizen is cost reduction through the elimination of
waste at all levels in the manufacturing process.
Kanban
Kanban stands for Kan- card, Ban- signal. The essence of the
Kanban concept is that a supplier or the warehouse should only
deliver components to the production line as and when they are
needed, so that there is no storage in the production area.
Within this system, workstations located along production lines
only produce/deliver desired components when they receive a
card and an empty container, indicating that more parts will be
needed in production
Kanbans are: 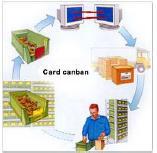
- Communication device; from the point of use to the previous
operation (customer to supplier)
- Purchase orders for suppliers
- Work order for manufacturing
- Visual communication tools
- Paperwork eliminators
Quality Functions Deployment (QFD)
QFD helps transform customer needs (the voice of the customer)
into engineering characteristics a product or service, prioritizing
each product or service characteristic while simultaneously
setting development targets for product or service.
QFD encourages organization to focus on the process itself
rather than just on the product or service By establishing
correlation between what is wanted and how it is to be delivered
, the vital aspects become more visible, aiding decision- making.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is methodology for
analyzing potential reliability problems early in the development
cycle where it is easier to take actions to overcome these issues,
thereby enhancing reliability through design. FMEA is used to
identify potential failure modes, determine their effect on the
operation of the product, and identify actions to mitigate the
failures. A crucial step is anticipating what might go wrong with
a product.
The types of FMEA are:
- System - focuses on global system functions
- Design - focuses on components and subsystems
- Process - focuses on manufacturing and assembly processes
- Service - focuses on service functions
- Software - focuses on software functions
Statistical Process Contorl (SPC)
SPC involves establishing the limits of statistical variability for a
system output parameter in steady state conditions. Limits for
the variability of the process are calculated and control limits
set, which mean that when not under steady state conditions
and the output variable either falls below the lower control limit,
or climbs a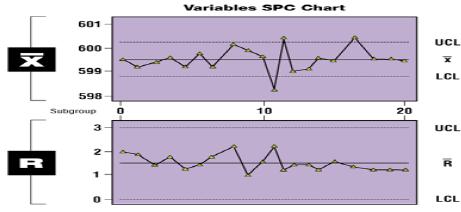 bove the upper control limit the process, In lean
manufacturing environments this is considered to be an
extremely effective quality tool, requiring only periodic bove the upper control limit the process, In lean
manufacturing environments this is considered to be an
extremely effective quality tool, requiring only periodic
measurement of system output variables, and thus low
administrative costs.
Machine capability studies
Machine capability studies are carried out using SPC techniques
to establish the statistical variability of an output parameter
from a machine in steady state conditions. If the engineering
tolerances required by products produced by the machine are
within its steady state limits of variability, the machine is said to
be "capable" of the tolerances.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is defined as "a program aimed at the near elimination
of defects from every product, process and transaction". O thers
defined it as a strategic initiative to boost profitability, increase thers
defined it as a strategic initiative to boost profitability, increase
market share and improve customer satisfaction through the use
of statistical tools that can lead to breakthrough quantum gains
in quality.
If deployed correctly, Six Sigma has the ability to generate a host
of benefits to business companies, e.g., improving process
speed, raising quality levels, reducing costs, increasing
revenues, and deepening customer relationships,
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
- Reduction in waste;
- Improvement in productivity and quality;
- Introduction of innovative practices for improving overall
competitiveness;
- Induce good management practices (GMP);
- Increase in manufacturing output
- Reduction in customer complaints
- Better and improved adherence to delivery schedule
- Reduction in quality rejection at every stage of production process
- Lesser inventory requirements at every stage of production
- Optimum utilization of resources in terms of space, manpower,
material, equipment utilization and energy consumption
- Orderly work place
- Imbibe a culture of continuous improvement
|
 ISO Consultants in Kolkata
ISO Consultants in Kolkata  Quality Foundation
Quality Foundation